Fundamental-Neuroscience-for-Neuroimaging
https://www.coursera.org/learn/neuroscience-neuroimaging/home/welcome
Anatomy
- Neurons 神经元细胞
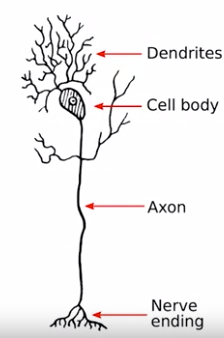
- Axon: transmits electrical signal 轴突
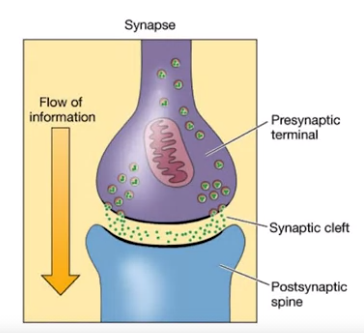
- axon terminal: = presynaptic terminal, end on adjoining dendrites or cell body
- Dendrites: receives contact 树突
- Glia 神经胶质细胞
- majority of cells
- function
- connective tissue
- metabolic support roles
- remove excessive secretions
- produces myelin=insulates neurons
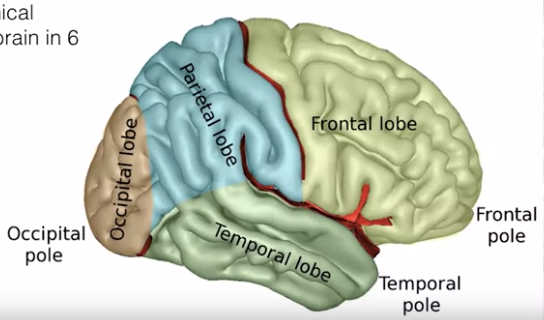
- Structural anatomy
- cytoarchitectural organization
- dissociable brain structure
- dissociable brain networks
- rudimental classification
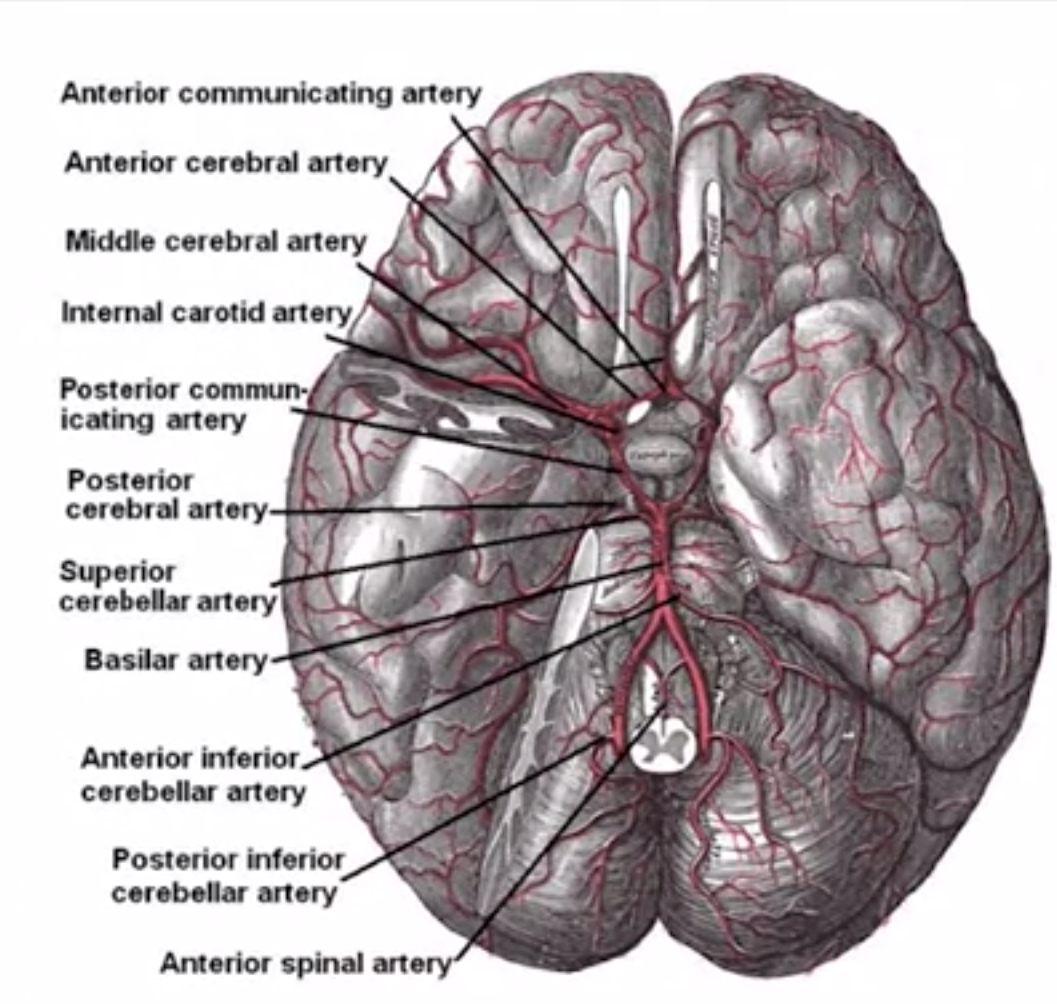
- vascular anatomy
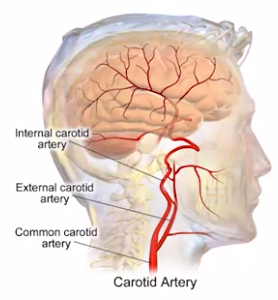
- circle of willis: blood enter brain
- anterior cerebral artery
- Similarity with other animals
- similar structure, human just bigger cortex
- allows experiment on simpler animals
- development stages
- cortex last
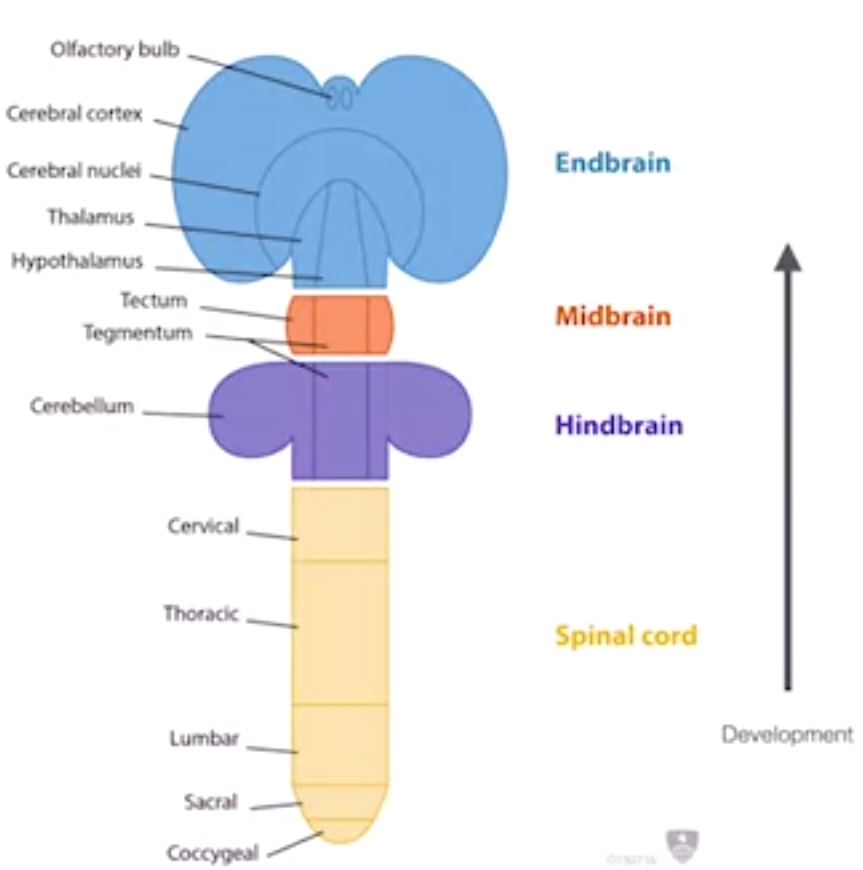
Terminology
-axis
-
Rostrum 嘴 cauda 尾
-
dorsal 背 ventrum 腹
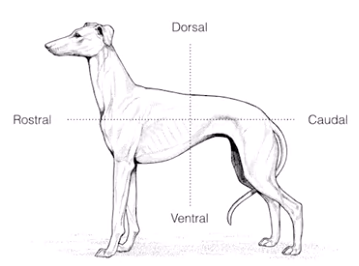
-
human
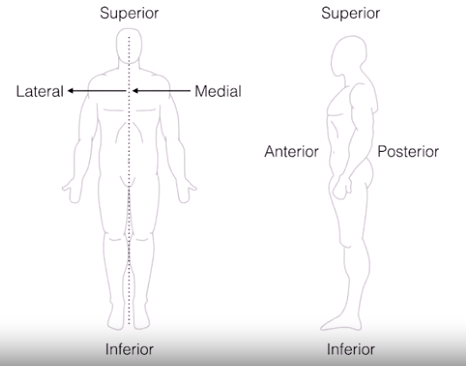
- superior - inferior
- antirior - posterior
- medial - lateral
-
planes
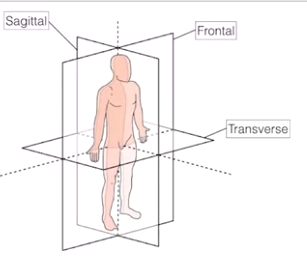
-
in MRI
- coronal = frontal
- axial - transverse
- sagittal
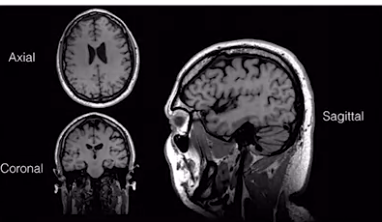
-
left vs right in frontal view
- radiological convention: left on right side of image
- face forward
- neurological convention: left is left in image
- face backward
- radiological convention: left on right side of image
-
use fiduciary marker - right side
-
-
proximal 近vs distal
-
ipsilateral 同側vs contralateral 異側
Methods of Communication in the Brain
-
reticular 网状 theory (Golgi)
- connected reticular net
-
neuron doctrine
- neurons are independent, contigual not continual
-
types:
- sensory neuron - external stimuli -> electrical signals
- interneuron - processing & relay
- motor neuron - electrical signals-> muscle or gland movement
-
ion channels & ion pumps
- influx of Ca++ -> synaptic vesicles fuse with pre-synaptic membrane
- transmitter released into cleft
- transmitter binds receptor molecules on post-synaptic membrane
- post-synaptic channels then open/close based on binding
- opneing -> influx of ions (Na+/K+) / close -> prevents
- causes either depolarize or hyper-polarize
- if post-synaptic voltage large enough -> electrochemical pual is generated = action potential
- simultaneously
- action potential travels down axon.
- used vesicle is retrieved and recycled
- new transmitter is synthesized
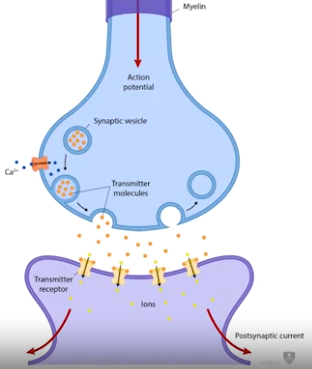
- Excitatory post-synaptic potential (EPSP)
- sometimes sum of EPSPs from multiple neuros are necessary for action potential
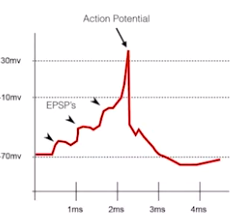
- sometimes sum of EPSPs from multiple neuros are necessary for action potential
- recording
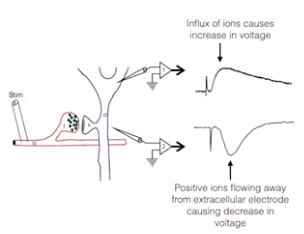
- inside neuron (1)
- outside neuron (2)
- extracellular eletrode can only measure local neuronal environment (local field potential LFP)
-
different neurotransmitters (>50)
- by makeup
- amino acids
- glutamate
- aspartate
- glycine ...
- peptides
- somatostatin ...
- others
- Serotonin 血清素
- Histamine 组胺
- Melatonin 褪黑素
- Norepinephrine 去甲肾上腺素
- amino acids
- by excitatory vs inhibooary
- excitatory
- epinephrine 肾上腺素
- norepinephrine
- inhibitory
- serotonin
- GABA
- both
- dopamine
- excitatory
- important examples
- acetylcholine 乙酰胆碱
- excitatory
- activates motor neurons
- attention, arounsal, learning, memory
- low levels in Alzheimers
- dopamine
- fine movements
- positive emotions
- abnorally low levels in Parkinsons
- abnorally high in frontal areas of schizophrenia
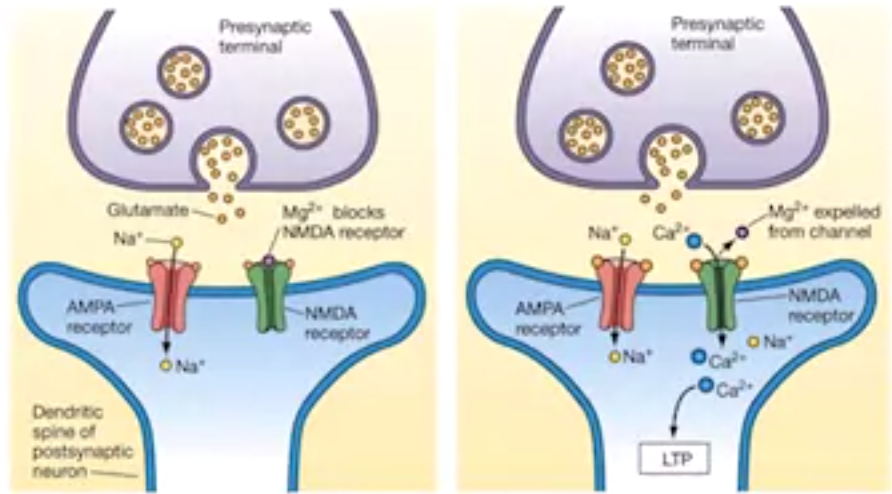
- glutamate 穀氨酸
- most commonly found
- learning & memory
- execessive production is toxic (ALS)
- binds to AMPA, open, allow Na+ in
- binds to NMDA, open, allow Ca++ in
- acetylcholine 乙酰胆碱
- different receptor react to different neurotransmitters
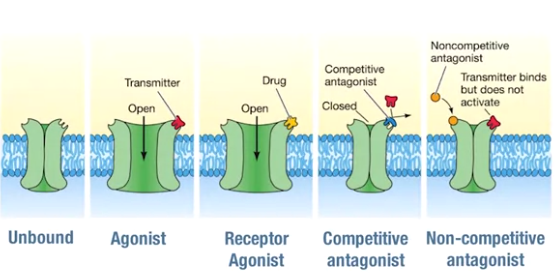
- agonist 激动剂
- competitive antagonist - blocks other agonist from binding
- non-competitive antagonist - different site
- by makeup
-
interaction with body
- direct innvervation through spinal cord + peripheral nerve system
-
cranial nerves
-
corticospinal tracts
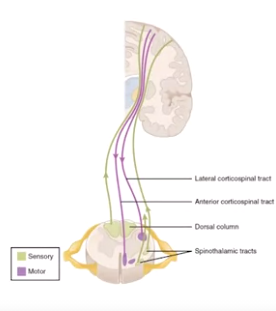
-
- through hormones in vascular system
- brain is neurochemically protected by BBB blood-brain barrier
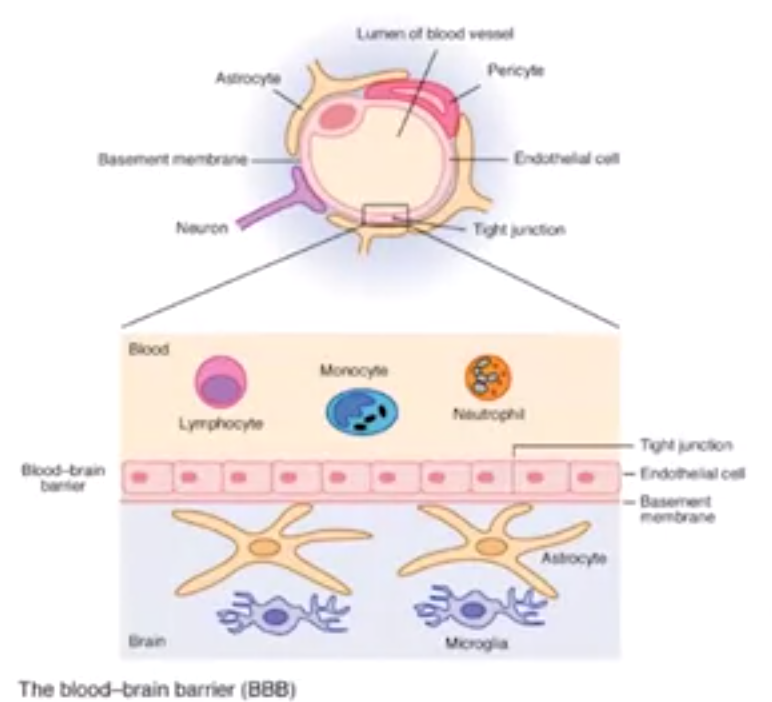
- endothelial cells line blood vessels
- needed material is actively transported, like glucose
- only small hydrophobic molecules e.g. O2 are allowed through
- prevents toxins, bacateria, etc.
- parts not protected by BBB:
- hypothalamus 下丘脑
- pituitary 脑下垂体
- pineal glands 松果体
- regulates temperature, thirst, hunger, circadian rhythm, sleep, stress response, etc.
- bi-directional
- e.g. adrenaline/epinephrine
- through blood, activates sympathetic nervous system 交感神经: fight/flight responses
- binds to receptors on vagal nerve -> releases glutamate -> encode the event to remember for future
- e.g. adrenaline/epinephrine
- brain is neurochemically protected by BBB blood-brain barrier
- direct innvervation through spinal cord + peripheral nerve system
Functional anatomy
-
cerebrospinal fluid CSF 脑脊液
- protects brain and spinal cord from trauma
- supply nutrients
-
grey matter
- contains neuronal cell bodies
- info processing
-
white matter
- fiber bundles of axon projects
- information transmission
-
primary motor cortex
- dorsal portion of frontal lobe
- plan movements
- send long axons down spinal cord
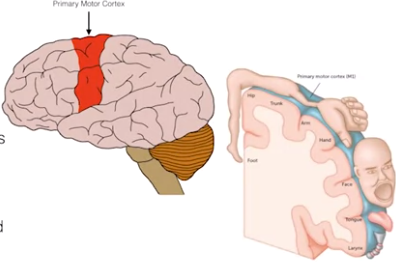
-
primary somatosensory cortex
- receives sensory input
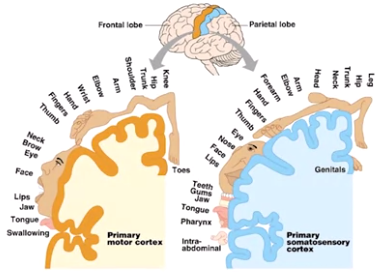
- amount of cortex is proportional to density of tactile receptors
-
thalamus 丘脑
- relay sensory and motor signal
- regulation of sleep and consciousness
-
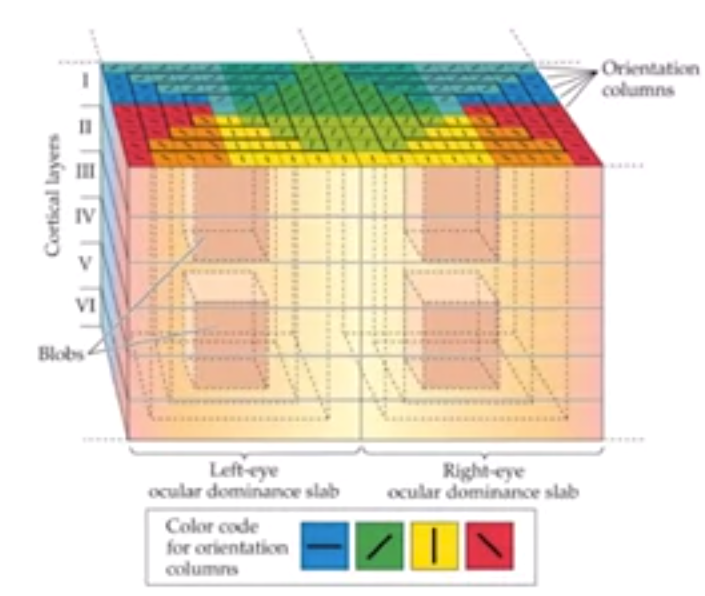
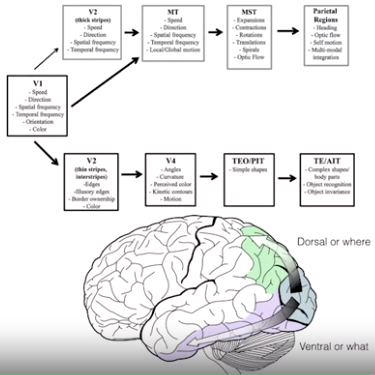
visual cortex
- orientation
- what or where pathway
- orientation
-
cerebellum 小脑
- seperate structure
- receive from sensory, spinal
- coordinates posture, balance, timing coordination
-
Organization of Cognitive Domains
- language
- Broca's aphasia
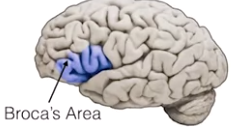
- understand words and simple sentences
- know what they want to say
- unable to generate fluent speech
- Wernicke area - silent, writing
- receptive aphasia
- unable to comprehend. can express
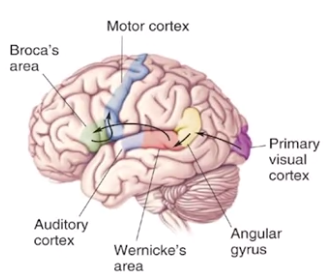
- Broca's aphasia
- Gage 1848 accident
- speech/motor still functions
- severe personality change
- memory
- patient H.M.
- removed bilateral hippocampus 海马体, amygdala 杏仁体 and surrounding cortext to fix seizure
- intact language, IQ, working memory and motor control
- unable to learn new facts/events
- unable to remember anything since the surgery
- but he's able to improve some motor skills (draw star) but don't consciously remember -> must be multiple area
- multiple systems
- medial temporal lobe
- basal ganglia 基底核
- fine motor planning and movements
- stratum: reward, reinforcement
- motor learning, stimulus response learning
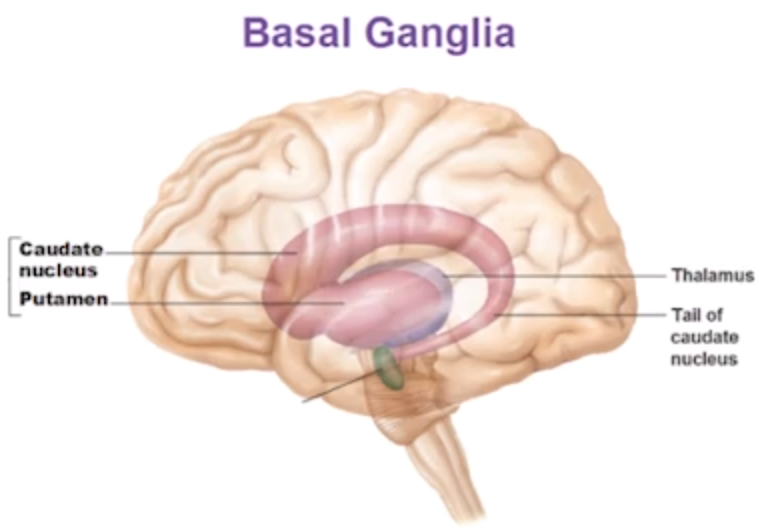
- patient H.M.
- specific tasks
- fusiform face area - recognizing faces
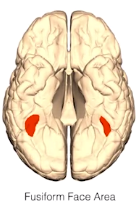
- fusiform face area - recognizing faces
- language
Neuropsychological Assessment of Cognition
Neuropsychology: behavioral expression of brain function
-
cognition
- initially: single function of intelligence. IQ=100 is median
-
emotionality
-
executive
-
Screening testing
- RBANS
- MMSE
- MOCA
-
Hypothesis testing
-
Neuropsychological battery approach
-
comprehensive
Example
- memory assessment
- Wechsler memory scale
- personal and current info
- orientation
- mental control
- logical memory
- digit span
- visual repro
- paired associate
- word list learning
- Wechsler memory scale
- Executive
- volition
- planning
- purposive action
- effective performance
- e.g. Stroop word test - word "red" colored in blue
Approaches to Neuroimaging
- Categories
- structural
- anatomy
- pathology
- functional
- metabolic
- pharmacologic
- cognitive
- structural
- techniques
-
EEG
- measure activity through electrodes on scalp
-
CT - computed axial tomography
- series of xrays
- many cross sections rescontructed to a 3D volume
- fast, but moderate radiation
-
single photoon emission computed tomograph - SPECT 单光子发射计算机断层成像术
- gamma emitter tracer through 静脉注射
- spacial resolution not good - a few cm
-
PET - positron emission tomography
- positron emitting radionuclide that binds to biologically active molecule
- FDG-PET: marker for glucose uptake (tumors, Alzheimers)
- 18F-AV-45 PET market for beta amyloid (protein occursi in Alzheimer's)
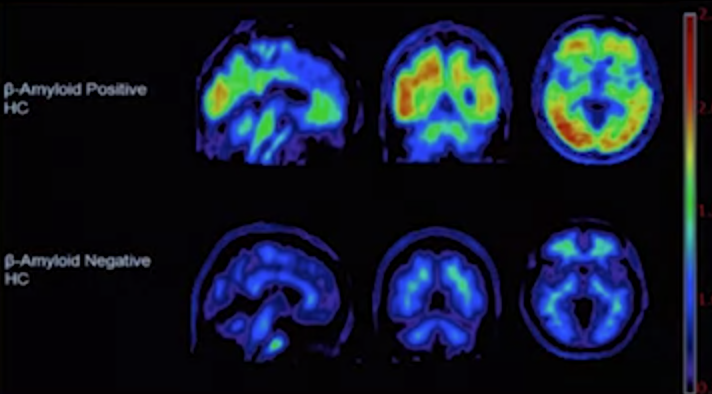
- detects pairs of gamma rays
- higher resolution than SPECT
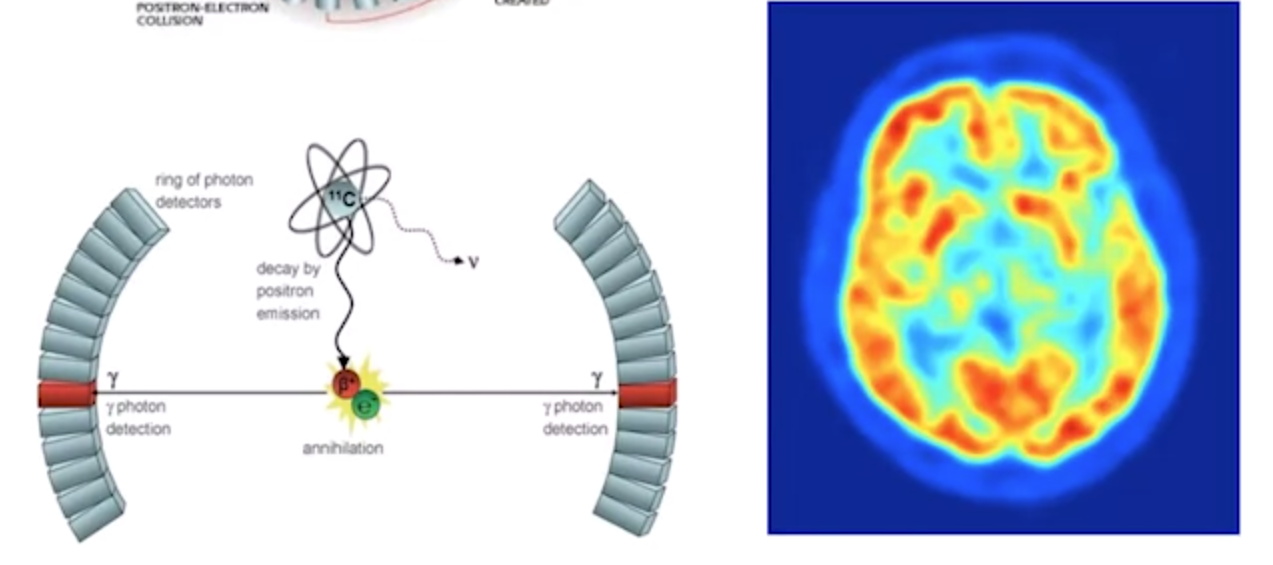
- positron emitting radionuclide that binds to biologically active molecule
-
MRI
- static + variable 磁场 perturb H atoms
- resulting resonance is masured by radio frequency receivers
- different pulse sequence -> different contrast for tissue type
- magnetic field is 60x stronger than earth
- ppl w pace maker should never do MRI
- dangerous to ave metallic objects in vicinity
- no radiation/known side effects
- high resolution
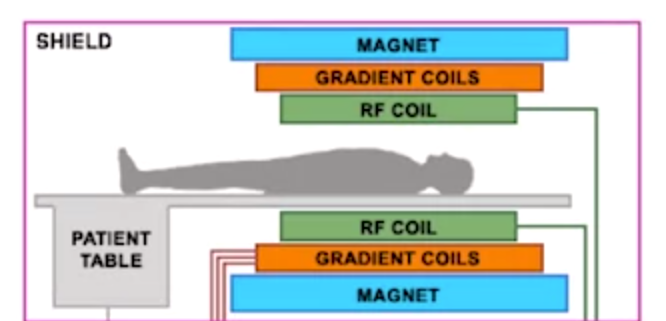
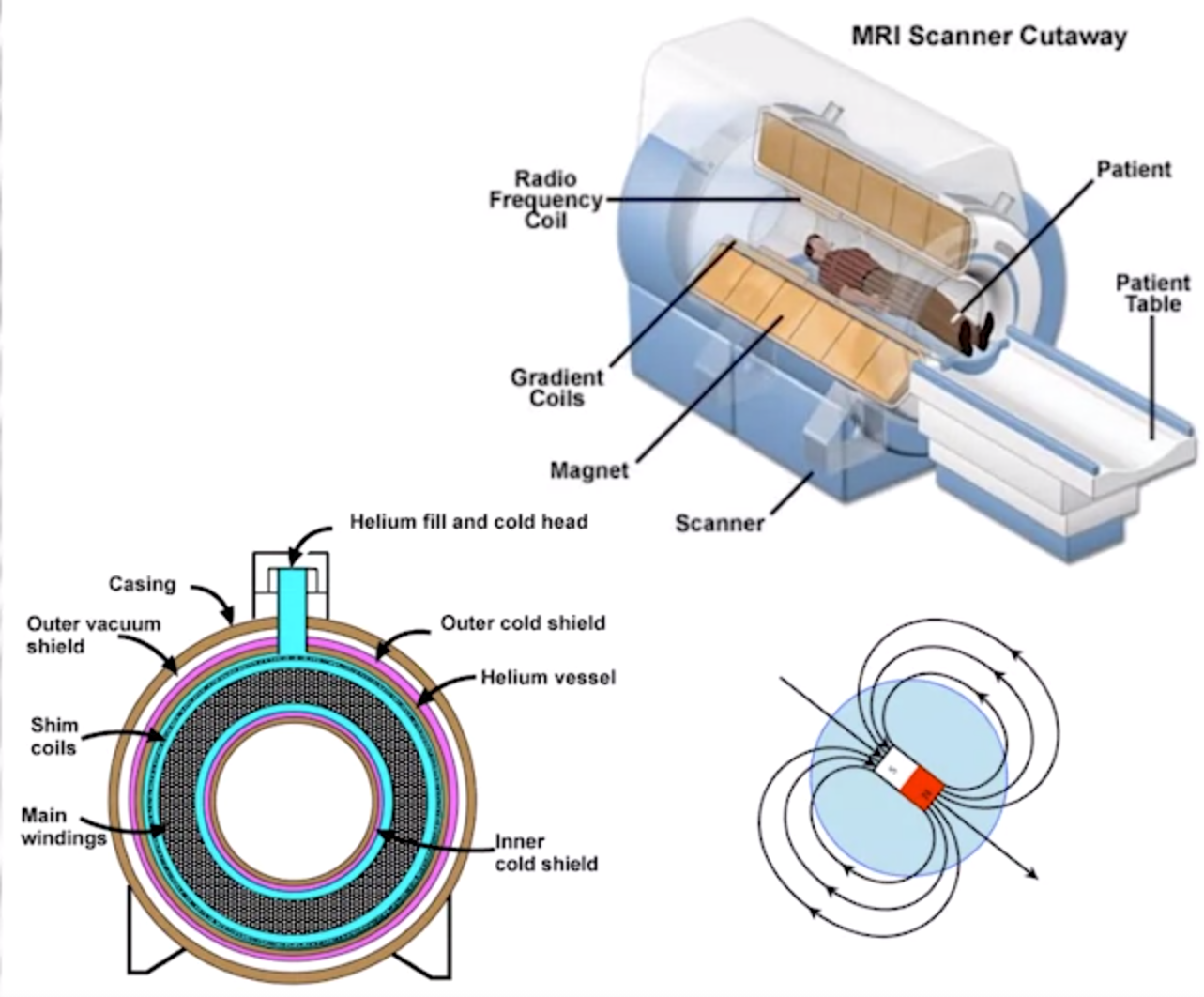
- -270C super conducting metal
- additional head antenae

-
fMRI
- magnetic resonance from oxygenated vs non-oxygenated blood
-
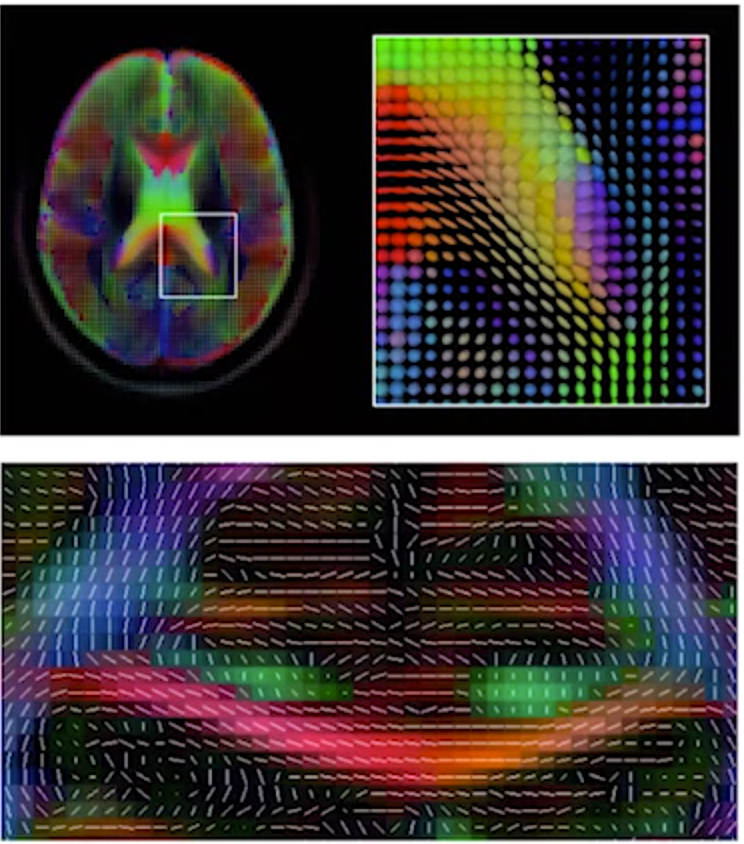
diffusion tensor imagining
- refined application of MRI
- measures directionality of water molecules
- assess fiber projecttions & white matter integrity
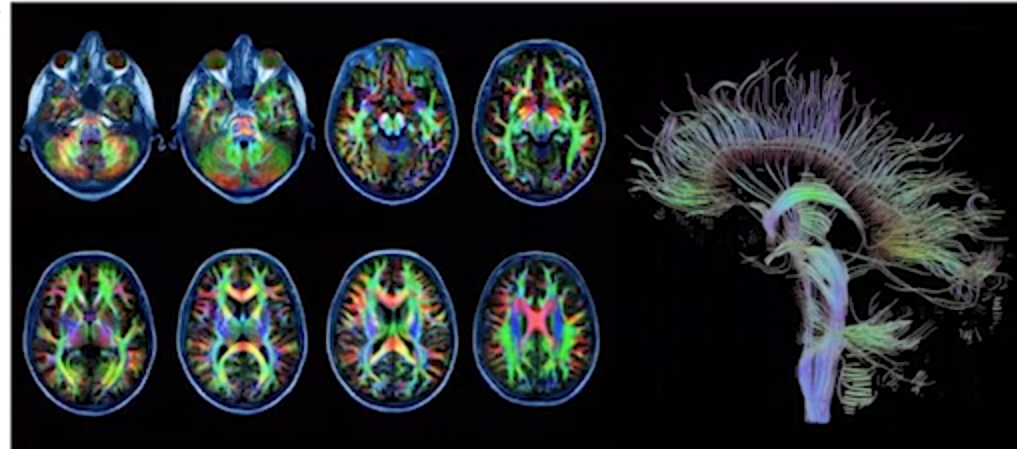
-
spectroscopy
- refined application of MRI
- magnetic signatures of various metabolites
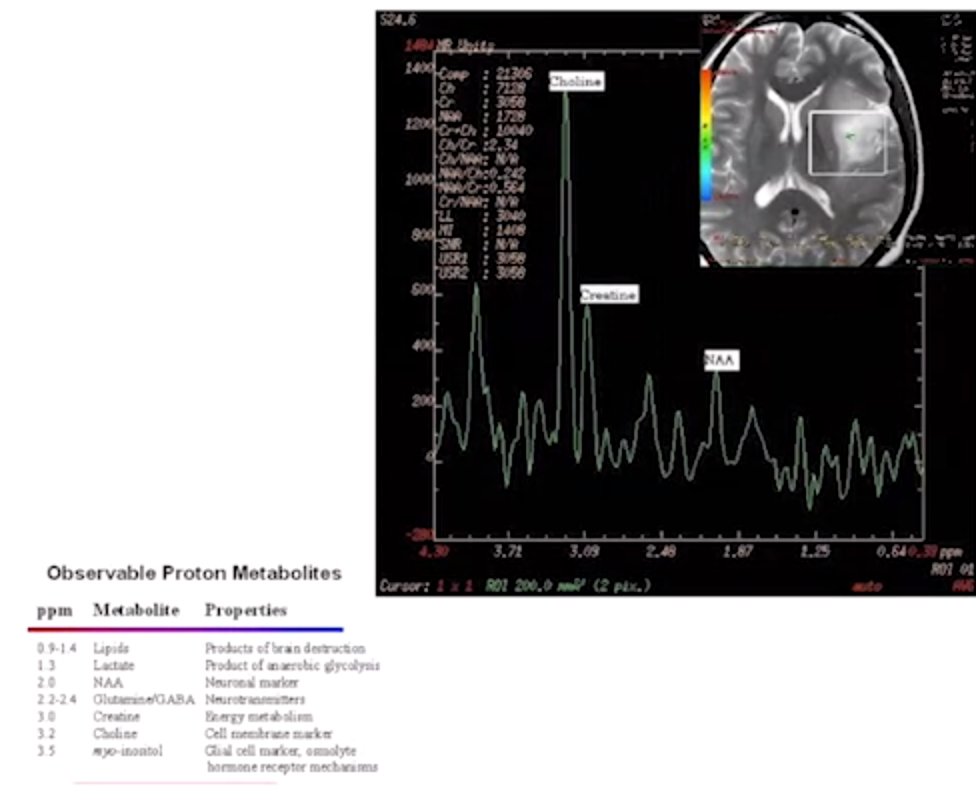
-
Basics of MRI
- MRI signal
- spin both its own axis and the magnetic field
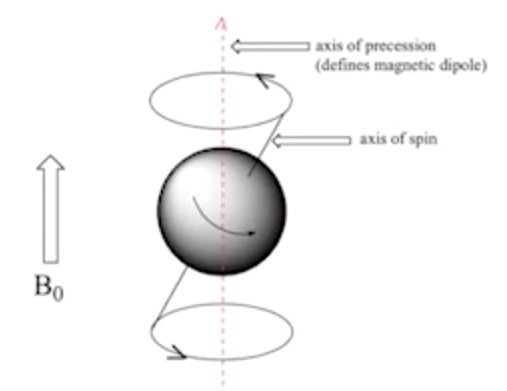
- parallel: low energy
- anti-parallel: high energy
- after a few seconds, reach equilibrium, all protons are aligned
- static field can't be measured. MRI signal introduces different direction perpendicular to the main field, causes protons to move away from axis
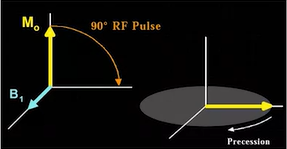
- when stops, procession back to original alignment
- t1 & t2 plane
- t1: longitutional (original field position)
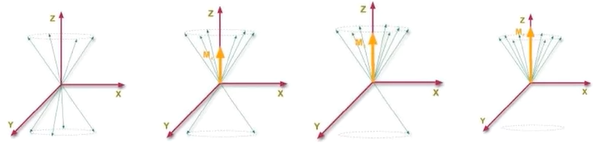
- t2: transverse
- t1: longitutional (original field position)
- the procession induces a signal in receiver coil
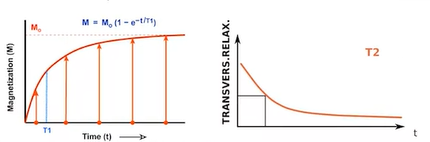
- relaxation time: time it takes to recover after being disturbed
- different biological matter have different but consistent t1 and t2 relaxation times
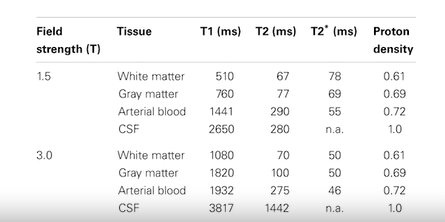
- tumor also different
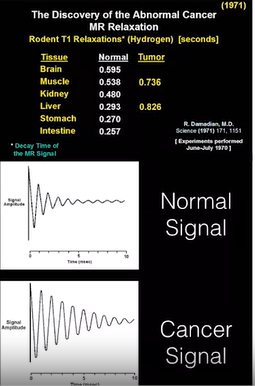
- tumor also different
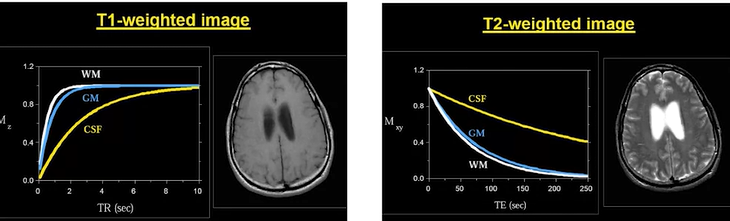
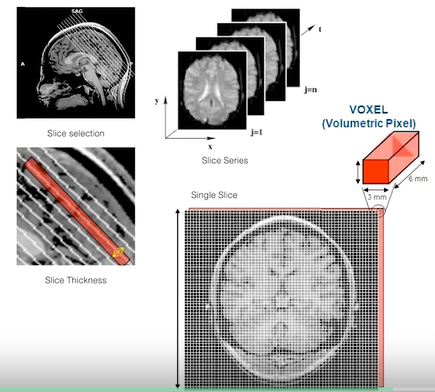
- spatial specificity
- Larmor frequency frequeny needed to changea spin from low to high energy spin
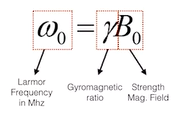
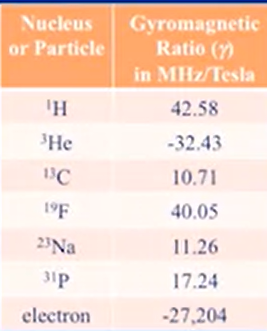
- MRI mostly targeting water molecules
- Larmor frequency depends on local magnetic strength
- create bands of frequency/magnetic gradient
- put together:
- linear gradients create sptial specificity
- radio purlse selectively excites slices
- Larmor frequency frequeny needed to changea spin from low to high energy spin
- spin both its own axis and the magnetic field
- fMRI
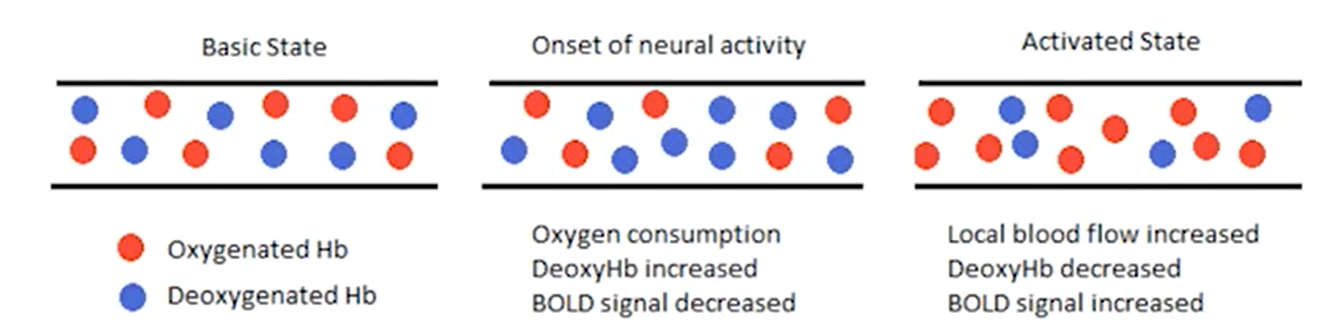
- oxygenated hemoglobin vs de-O hemoglobin have different effects on dephasing - de-O hemoglobin cause more dephasing
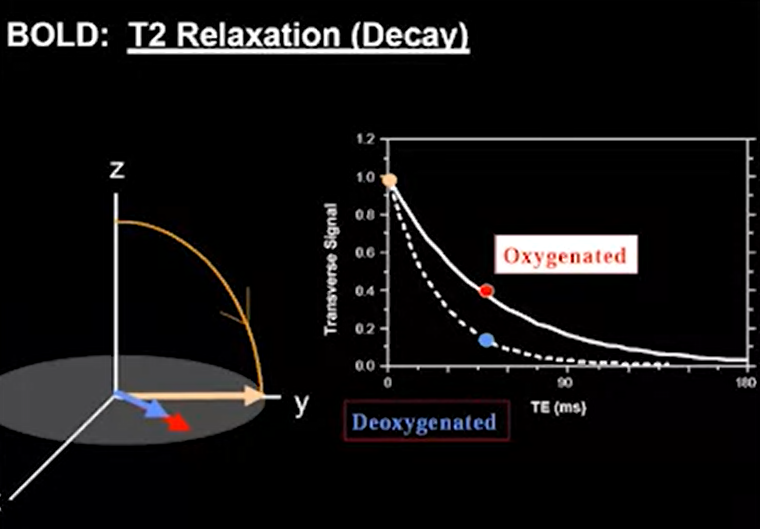
- Blood Oxygen Level Dependent (BOLD) MRI
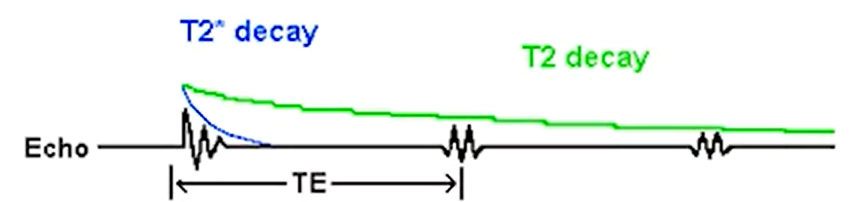
- measure changes in homogeneity in magnetic field (T2*)
- T2: transverse magnetization decay of a spin after radio frequency pulse
- T2*: transverse magnetization decay from local magnetic field variations
- de-O hemoglobin: paramagnetic, introduces inhomogeneity
- O hemoglobin: little effect
- BOLD signal:
- HRF: hemodynamic response function
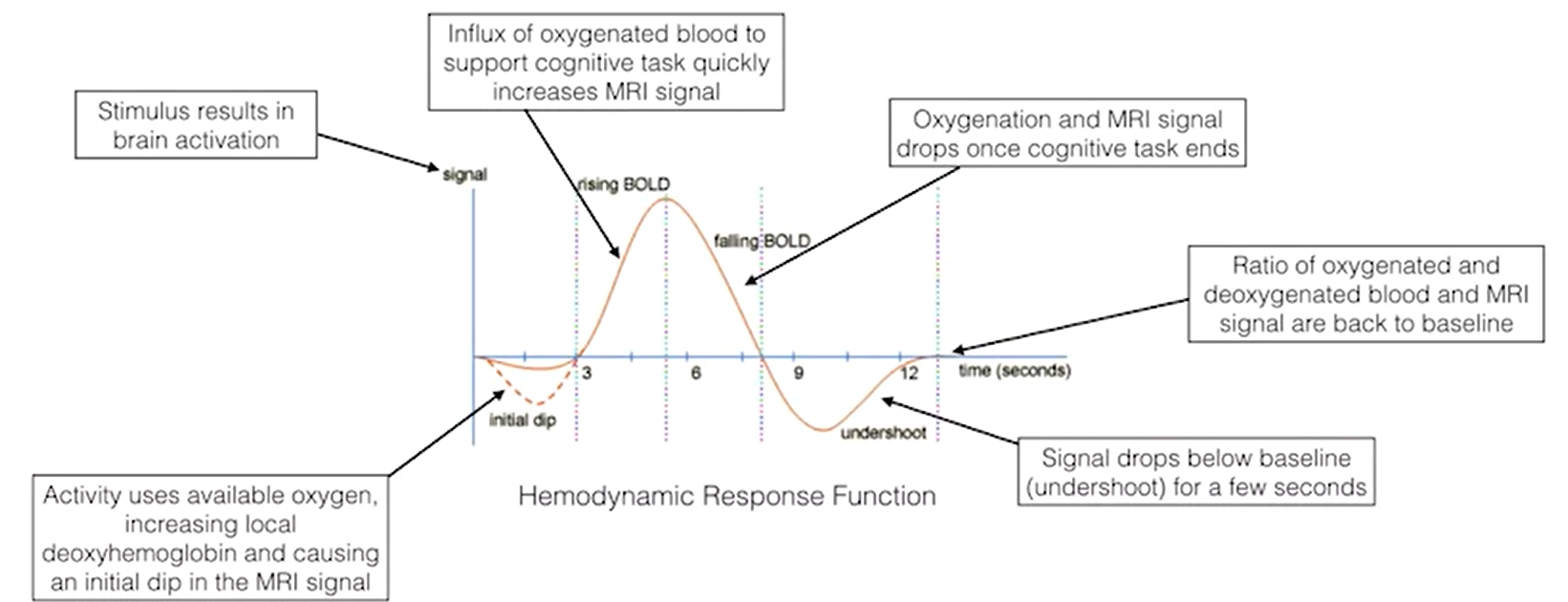
- it doesn't measure neural activity directly
- measures metabolic demands
- HRF: hemodynamic response function
- physiological basis:
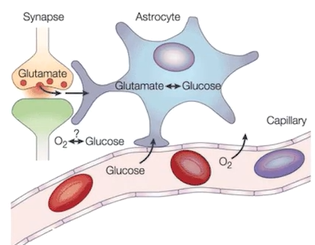
- glutamate releases
- open post-synaptic ion channels
- re-uptake of glutamate by astrocyte triggers glucose metabolism
- astrocytes pump out ions to restor ionic gradients
- processes use glucose + O2
- MUA- multi-unit activity
- LFP local field potential = summation of post-synaptic potential more correlated (but delayed) w BOLD activity
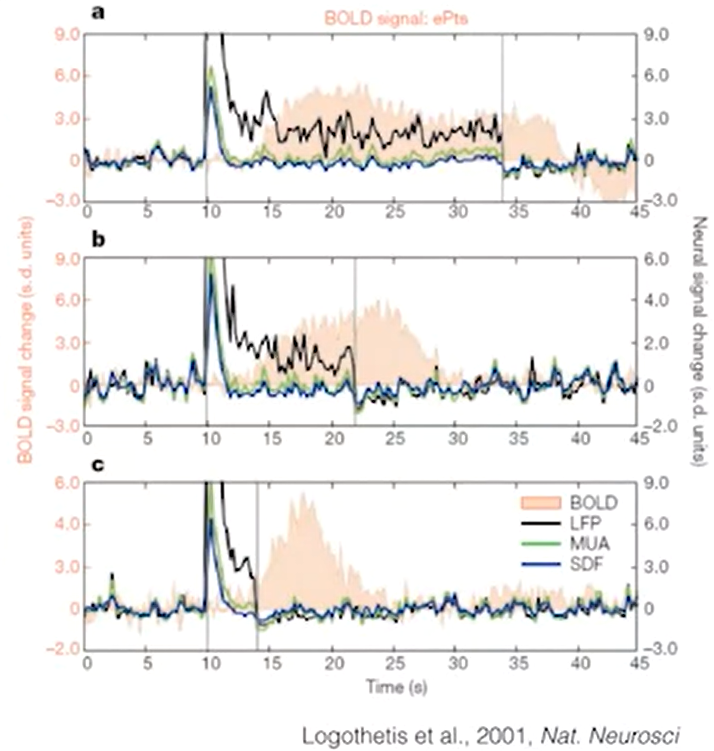
MRI studies
-
structural
-
qualitative eval
-
volumetric analysis:
- count voxels -> difference of volume of various parts compared to controls
- automatic segmentation
-
analyze cortical thickness
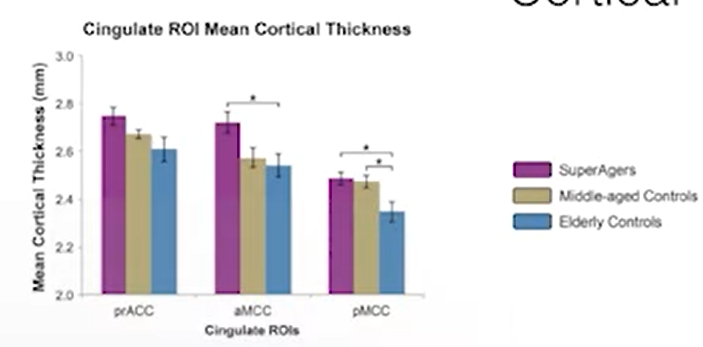
-
strutural morphology: compare shape differences
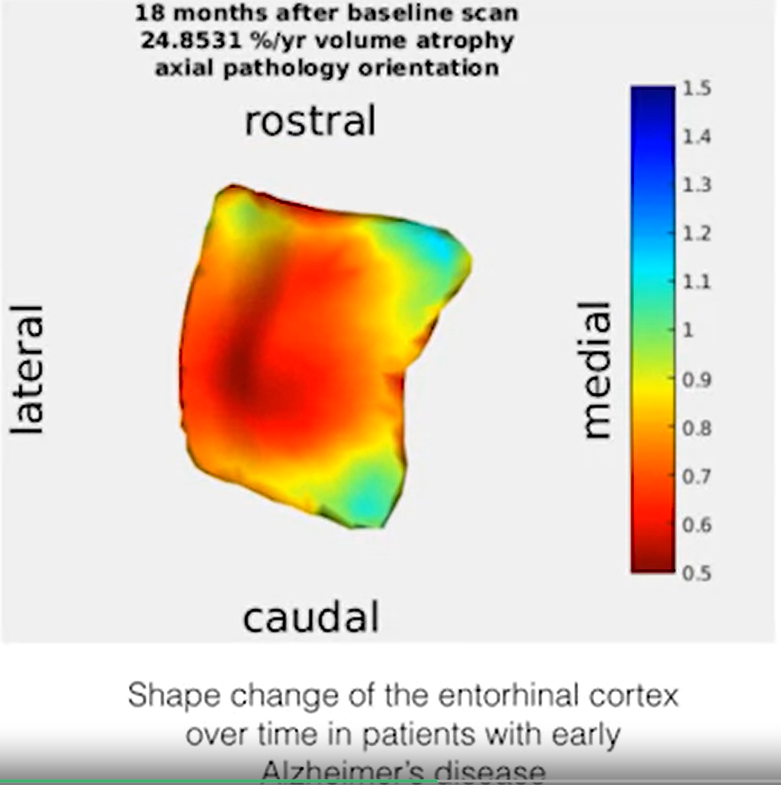
-
example of correlating behavioral w structual analysis:
-
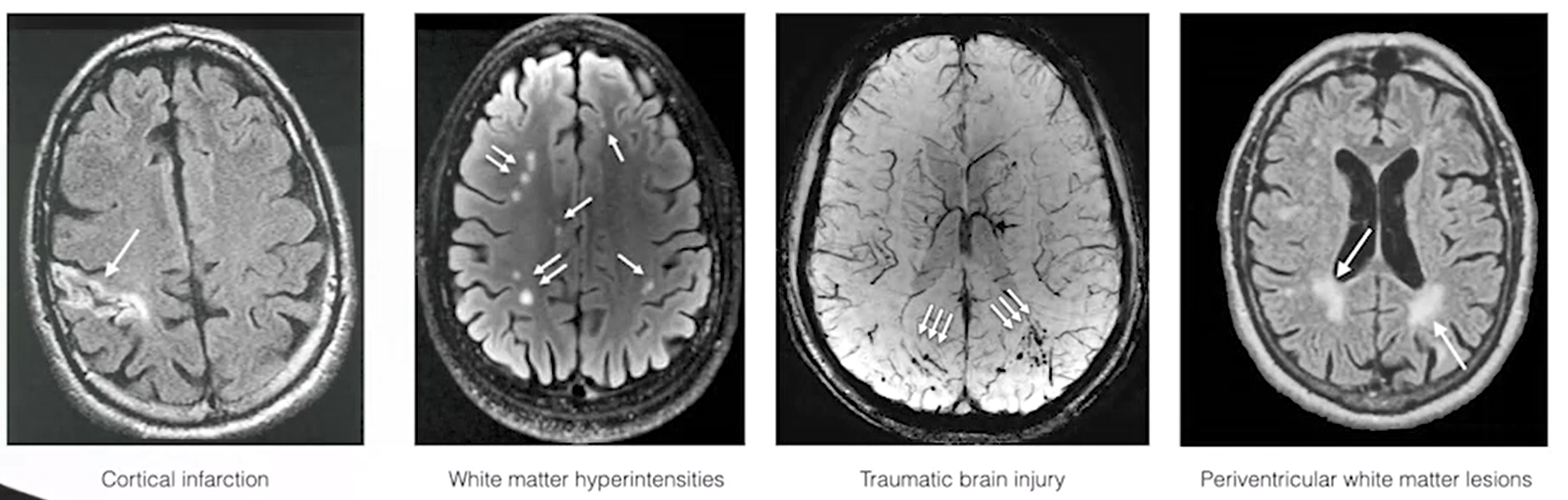
many reasons for structural brain changes:
- development/atrophy
- exercise
- substance use
- inflammation / edema
- gliosis
-
-
fMRI studies
- spatial resolution: 1-1.5 mm
- temperal resolution ~0.5 sec
- no long lasting effects
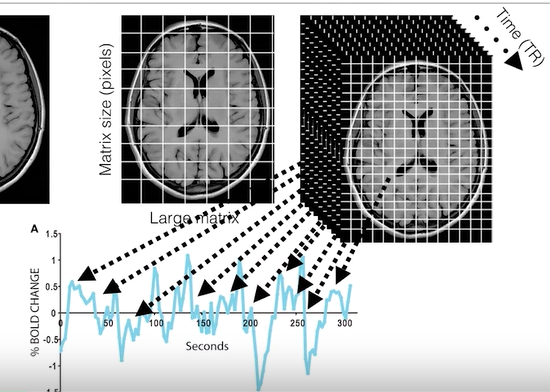
- block of epoch design
- repetitive on and off time
- simple to design, robust activation due to large number of trials
- con:
- assume single mode of activiation at consistant level over repititions
- event related design
- pro:
- flexible analysis
- con:
- reduced detection power
- sensitive errors in hemodynmaic response function
- pro:
- cognitive subtraction
- assumption: different cognitive components are additive
- subtract activitation of control task from that of experiment task can isolate effects of that difference in task (taskA-taskB)
- subtraction is only valid if condition differs in only one property
- e.g. using resting condition as control is bad
- When zero is not zero: the problem of ambiguous baseline conditions in fMRI
- find face recognition

Experimental design
technical limitation
- limited visual field + response options
- scanner drift - each runs limit to 4-6 min, then restart
- longer will cause heat up, change accuracy
- subject motion: - mm movmement change will interfere psychological state
psychological state
- is the subject effectively engaged?
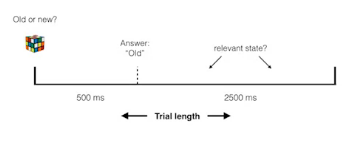
- after subject answers, maybe mind drifts off to think about other things
- are they using shortcuts to solve the problem?
- how long does the psychological state last
- does the task induce unintended psych state?
- e.g. get anxious or frustrated
statistical design
- substraction
- factorial
- multiple factors & interaction

- multiple factors & interaction
- parametic
- increase levels of difficulty
- measure before/after intervention e.g. drug/training/therapy
Functional connectivity MRI
- Hebbian principle: cells fire together, wire together
- spatial correlation vs temporal correlations
- voxel to voxel connectivity
- compare every voxel against every other
- seed based connectivity
- pick an area, compare other areas with that
- independent componenet analysis
- how many independent networks are at work?
- DMN default mode network
- highly correlated during wakeful rest
- less active of external task
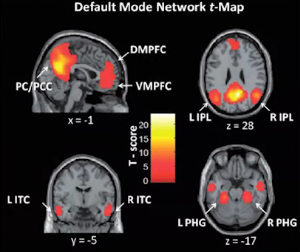
- developmentally established:
- more developed as kid grows up
- overlap with structural connectivity
- neurological basis of self, self-reference, theory of mind, social cognition
- support comprehension, learning, memory
- support thinking of past and future
- deactivation of DMN correlate:
- memory encoding
- task difficulty
- activiation of DMN after learning improves memory
- connectivity in DMN observed in
- alzheimer's
- autism
- depression
- aging
- schizophrenia
- epilepsy
- OCD
- anoerexia nervosa ...
- DMN default mode network
- how many independent networks are at work?
Diffusion Tensor Imaging
-
Hydrogen
-
unpaired proton -> magnetic properties, sutied to disturb the local static mag field
-
unibiquitous - water & fat issue
-
water diffusion:
- isotropic: all directions
- anisotropic: has dimensionality
-
brain
- grey matter - cell bodies- isotropic
- white matter - axon - anisotropic
-
DTI:
-
gradient pulses
- cancel out for stationary H2O
- lack of signal for diffusing molecules
-
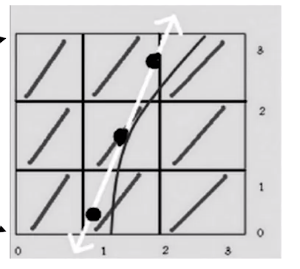
for each voxel, find the eigenvalues for each eigenvector
-
probablistic fiber tracking
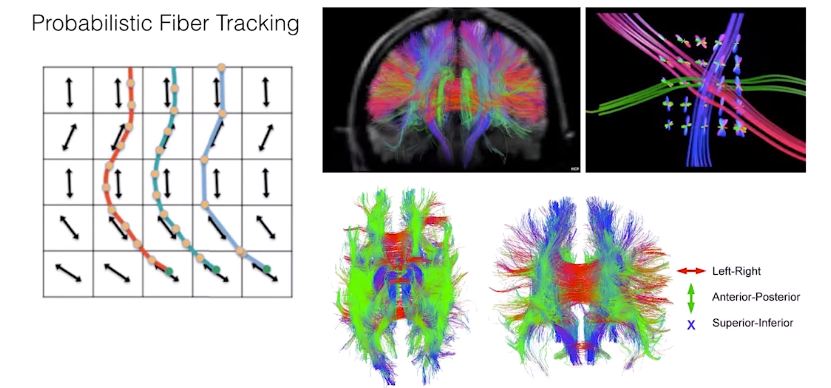
-
-
studies
- fractional anisotropy
- 0: isotropic diffusion
- 1: diffusion in 1 direction
- measure
- fiber density
- white matter integrity
- FA correlation with symptoms
- e.g. OCD
- DTI tracography in surgical planning
- tumor removal planning
- eletrode simulation
- fractional anisotropy
Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy
-
processions causes a small local magnetic field, opposite direction of static mag field
-
change the local effective mag field, causes resonance frequency to shift "chemical shift"
- value of the shift gives info about the molecular group of that nucleaus
- MRS quantify local presence of certain chemical compounds
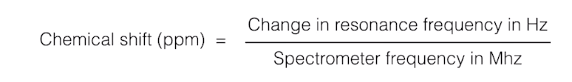
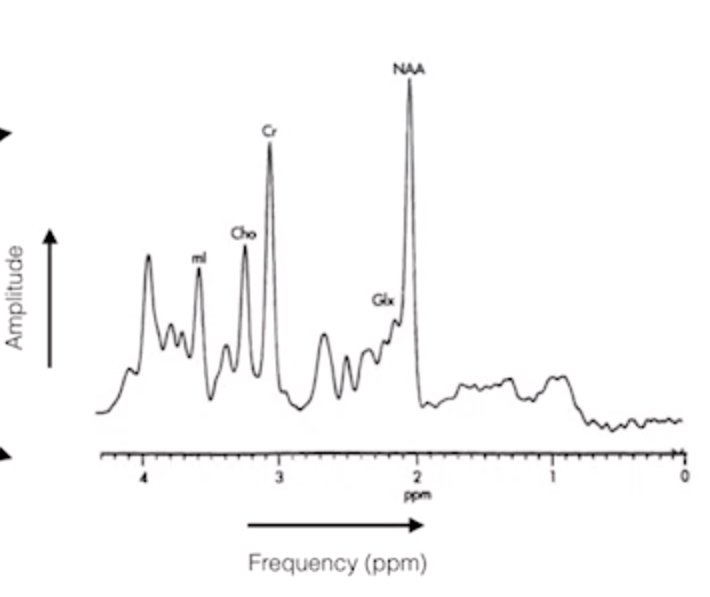
- spectra can be obtained from different nuclei but H most common
-
water signal must be suppressed
- Chemical Shift Selective suppression pre-saturate water signal using spepcifc pulse frequency
-
sepctra provide metabolite concentration in different area of brain
-
common metabolite
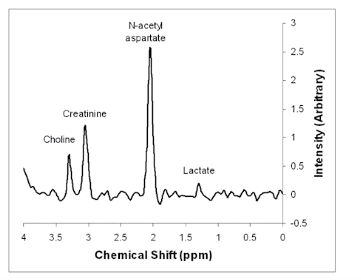
- NAA N-acetylaspartate
- normally highest peak in normal brain
- decrease <-> white matter disease, malignant neoplasms
- Cr creatine
- marker for energetic system and intracelluar metabolism
- reduced siganal in tumors
- Cho Choline
- marker of celluar membrane turnover - cellular proliration
- incrase in infarction梗塞/inflammation
- LacLactate
- marker of anerobic metabolism, e.g. cerebral hypoxia, ischemia, seizures, metabolic disorders,
- occur in cysts, normal pressure hydrocephalus 腦積水, certain tumors
- NAA N-acetylaspartate
-
clinally:
- most used in brain tumors, metabolic disorders
book recommendations
- Principles of Neural science - Kandel, schwartz