Spring in Action
Chpt 2: Wiring beans
Auto configuration
@Autowiredworks on both constructor and method (will create dependent beans, and throw error if can't find)@Autowiredis spring specific, use@Injectfrom java, mostly interchangable- when using
@ComponentScan, better to usebasePackageClassesto be refactor proof
Manual wiring:
-
@beanby default ID = method name. override it withname= -
by default, all beans in spring are singletons.
@Bean public CompactDisc sgtPeppers(){ return new SgtPappers(); }if directly call the method that a bean annotation is on, e.g.
sgtPepeprs()will return the singleton rather than creating another instance.Chpt 3: Advanced wiring
-
@Profile("dev")annotation for beans only created when active profiles include dev -
@Conditional(MagicExistsCondition.class)for custom conditions- Condition interface comes with 2 params:
matches(ConditionContext context, AnnotatedTypeMetadata metadata) - ConditionContext
- bean registry: bean definitions
- bean factory: presence of beans
- environment: env varialbes
- resource loader: resources loaded
- class loader: class loaded
- Condition interface comes with 2 params:
-
disambiguating beans
-
@Primary -
@Qualifier("cold) -
Use custom qualifier annotations to allow multiple qualifiers -
@Cold@Target({ElementType.FIELD, ElementType.PARAMETER, ElementType.TYPE}) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Qualifier public @interface Cold { }
-
-
@Scope- singleton
- prototype - created each time is injected
- session - in web app, one for each session. e.g. shopping cart
- request
- scope proxy
Chpt4: Aspect oriented Spring
-
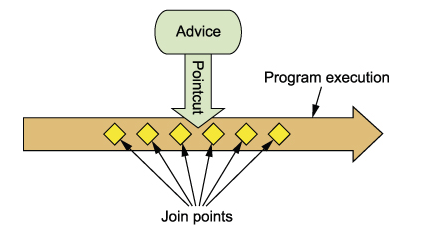
basic concepts:
-
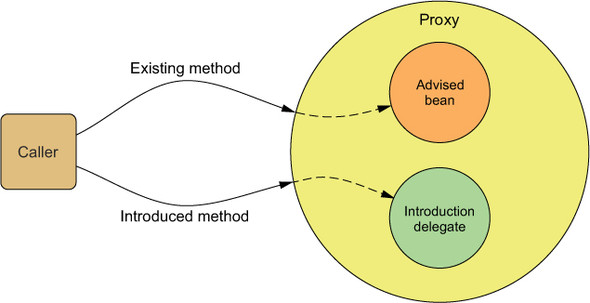
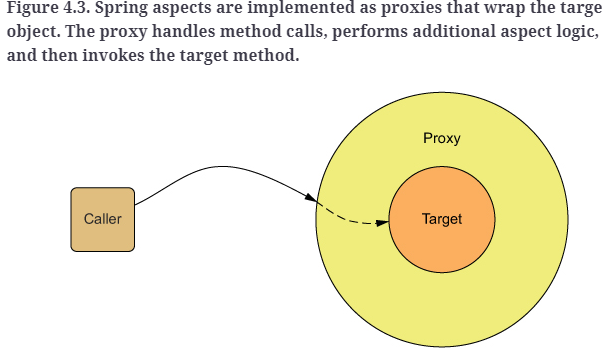
unlike AspectJ, spring is proxy based, and only supports method interception
-
wrap method options:
@After@AfterReturning@AfterThrowing@Around@Before
-
also possible to add methods using Introduction