Week2 - ArcGIS Basics
Using ArcMap for data exploration
-
right click 'Identify' to look at attributes for one item
-
or multi select -> Right click on layer -> open attribute table, to see attributes of the multiple selection
-
Add a basemap for reference and change transparency (Layer Property -> Display) of the new layer to explore to overlay on top of basemap
-
Right click on layer -> Data -> item description to read metadata about the file
-
Layer property
- scale dependent rendering: don't show when scale > x
- Choose grouping and color ramp;
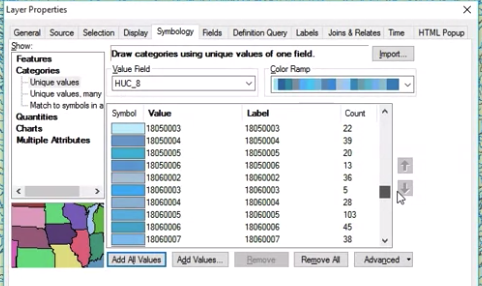
- Definition query: e.g. "CumulativeArea.TotDASqKM > 5"
- Labels - choose label field
-
Select by attribute:
- query:
- use "Get Unique Values" to help find value options for query
- string matching
GNIS_NAME LIKE '%Sacramento River'
- layer -> zoom to selection
- query:
-
Calculate geometry
- to find sum of length of rivers named X: select by atttribute -> create a new column -> calculate geometry -> statistics on the column
-
Select by location
- after selecting some regions -> Select by location -> can find things in another layer that intersects/within/centroid lands in/ + add a radius... with the current selection
-
Export the selected data for future
Projections
- Datum - fixed reference point for coordinates
- Geographic coordinate systems
- Projected coordinate system
- conformal - preserves local shape
- equal area - preserves area
- equidistant - preserve distances between points
- common projections
- equirectagular: equal constant distance between parallels and meridians
- Mercator (conformal): angles preservation, good for navigation, standard for web, optimized for calculation speed
- Mollweide (equal area): relative area preserved but shape distorted
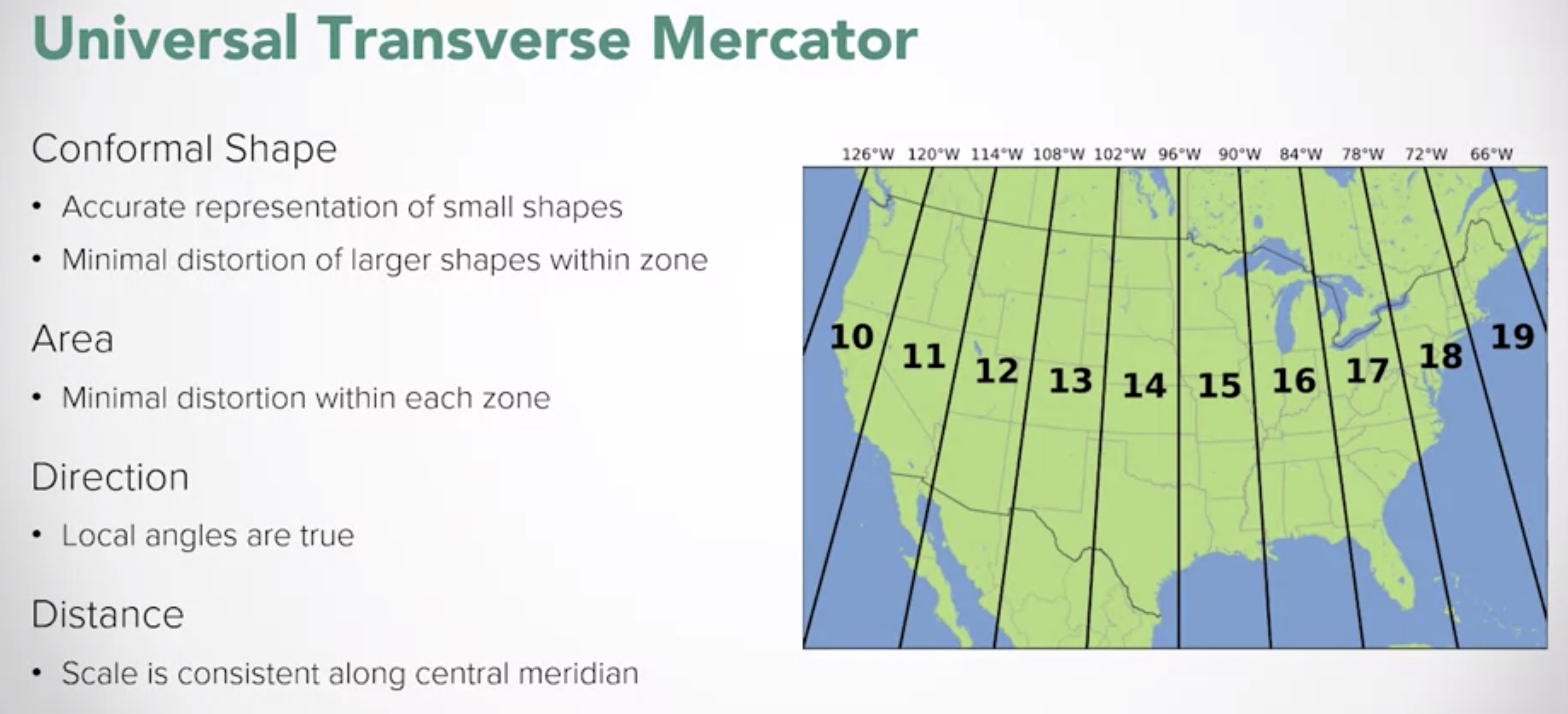
- Universal Transverse Mercator
Geoprocessing
-
Geoprocessing tool box:
- Union: join two features (e.g. take NA map and SA map into a hemisphere map)
-
Environment variables
- change projections
- Processing extent: limit the area to do analysis
-
Spatial Join Tool
-
ArcToolbox -> Analysis Tools -> Overlay -> Spatial Join
-
JOIN_ONE_TO_ONE: use merge rule (e.g. join counties to watershed, but each watershed may go across multiple counties)
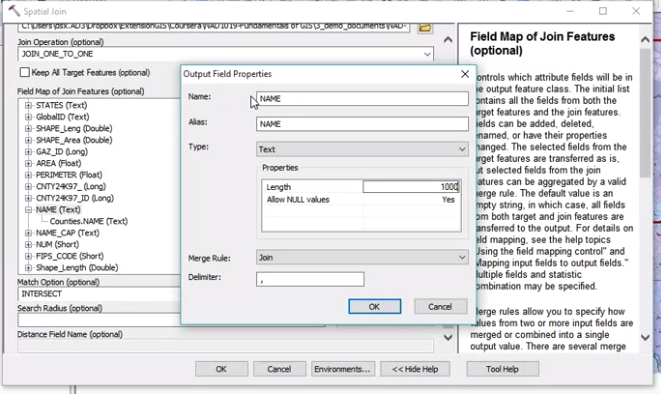
-
JOIN_ONE_TO_MANY: each watershet + county is a new row
-
example uses:
- use it for summarizaiton
- which road cross a river
- join multiple layers (e.g. electoral district + water + utility )
-